Salicylic Acid Shampoo: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Dosage form: shampoo
Drug classes: Topical acne agents, Topical keratolytics
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Mar 25, 2024.
On This Page
Salicylic Acid Shampoo Description
Salicylic Acid Shampoo, 6% (w/w) contains salicylic acid USP, in a vehicle consisting of acrylates copolymer, behentrimonium chloride, cocamidopropyl betaine, disodium EDTA, glycerin, isopropyl alcohol, methylparaben, propylene glycol, propylparaben, purified water, quaternium 26, sodium laureth sulfate, and trolamine.
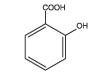
Salicylic acid is the 2-hydroxy derivative of benzoic acid with the following structure:
Salicylic Acid Shampoo - Clinical Pharmacology
Salicylic acid has been shown to produce desquamation of the horny layer of skin while not effecting qualitative or quantitative changes in the structure of the viable epidermis. The mechanism of action has been attributed to a dissolution of intercellular cement substance. In a study of the percutaneous absorption of salicylic acid in a 6% salicylic acid gel in four patients with extensive active psoriasis, Taylor and Halprin showed that the peak serum salicylate levels never exceeded 5 mg/100 ml even though more than 60% of the applied salicylic acid was absorbed. Systemic toxic reactions are usually associated with much higher serum levels (30 to 40 mg/100 ml). Peak serum levels occurred within five hours of the topical application under occlusion. The sites were occluded for 10 hours over the entire body surface below the neck. Since salicylates are distributed in the extracellular space, patients with a contracted extracellular space due to dehydration or diuretics have higher salicylate levels than those with a normal extracellular space (see PRECAUTIONS).
The major metabolites identified in the urine after topical administration are salicyluric acid (52%), salicylate glucuronides (42%) and free salicylic acid (6%). The urinary metabolites after percutaneous absorption differ from those after oral salicylate administration; those derived from percutaneous absorption contain more salicylate glucuronides and less salicyluric and salicylic acid. Almost 95% of a single dose of salicylate is excreted within 24 hours of its entrance into the extracellular space.
Fifty to eighty percent of salicylate is protein bound to albumin. Salicylates compete with the binding of several drugs and can modify the action of these drugs; by similar competitive mechanisms other drugs can influence the serum levels of salicylate (see PRECAUTIONS).
Indications and Usage for Salicylic Acid Shampoo
For Dermatologic Use: Salicylic Acid Shampoo, 6% is a topical aid in the removal of excessive keratin in hyperkeratotic skin disorders, including verrucae, and the various ichthyoses (vulgaris, sex-linked and lamellar), keratosis palmaris and plantaris, keratosis pilaris, pityriasis rubra pilaris, and psoriasis (including body, scalp, palms and soles).
For Podiatric Use: Salicylic Acid Shampoo, 6% is a topical aid in the removal of excessive keratin on dorsal and plantar hyperkeratotic lesions. Topical preparations of 6% salicylic acid have been reported to be useful adjunctive therapy for verrucae plantares.
Contraindications
Salicylic Acid Shampoo, 6% should not be used in any patient known to be sensitive to salicylic acid or any other listed ingredients. Salicylic Acid Shampoo, 6% should not be used in children under two years of age.
Warnings
Prolonged use over large areas, especially in children and those patients with significant renal or hepatic impairment could result in salicylism. Excessive application of the product other than is needed to cover the affected area will not result in a more therapeutic benefit. Concomitant use of other drugs which may contribute to elevated serum salicylate levels should be avoided where the potential for toxicity is present. In children under 12 years of age and those patients with renal or hepatic impairment, the area to be treated should be limited and the patient monitored closely for signs of salicylate toxicity: nausea, vomiting, dizziness, loss of hearing, tinnitus, lethargy, hyperpnea, diarrhea, and psychic disturbances. In the event of salicylic acid toxicity, the use of salicylic acid should be discontinued. Fluids should be administered to promote urinary excretion. Treatment with sodium bicarbonate (oral or intravenous) should be instituted as appropriate. Patients should be cautioned against the use of oral aspirin and other salicylate containing medications, such as sports injury creams, to avoid additional excessive exposure to salicylic acid. Where needed, aspirin should be replaced by an alternative non-steroidal, anti-inflammatory agent that is not salicylate based.
Due to the potential risk of developing Reye’s syndrome, salicylate products should not be used in children and teenagers with varicella or influenza, unless directed by a physician.
Drug Interactions
The following interactions are from a published review and include reports concerning both oral and topical salicylate administration. The relationship of these interactions to the use of salicylic acid is not known.
I. Due to the competition of salicylate with other drugs for binding to serum albumin the following drug interactions may occur:
|
DRUG |
DESCRIPTION OF INTERACTION |
|
Sulfonylureas |
Hypoglycemia potentiated. |
|
Methotrexate |
Decreases tubular reabsorption; clinical toxicity from methotrexate can result. |
|
Oral Anticoagulants |
Increased bleeding. |
II. Drugs changing salicylate levels by altering renal tubular reabsorption:
|
DRUG |
DESCRIPTION OF INTERACTION |
|
Corticosteroids |
Decreases plasma salicylate level; tapering doses of steroids may promote salicylism. |
|
Acidifying Agents |
Increases plasma salicylate level. |
|
Alkanizing Agents |
Decreased plasma salicylate levels. |
III. Drugs with complicated interactions with salicylates:
|
DRUG |
DESCRIPTION OF INTERACTION |
|
Heparin |
Salicylate decreases platelet adhesiveness and interferes with hemostasis in heparin treated patients. |
|
Pyrazinamide |
Inhibits pyrazinamide induced hyperuricemia. |
|
Uricosuric Agents |
Effect of probenemide, sulfinpyrazone and phenylbutazone inhibited. |
The following alterations of laboratory tests have been reported during salicylate therapy:
|
LABORATORY TESTS |
EFFECT OF SALICYLATES |
|
Thyroid Function |
Decreased PBI; increased T3 uptake. |
|
Urinary Sugar |
False negative with glucose oxidase; false positive with Clinitest with high-dose salicylate therapy (2-5g q.d.). |
|
5-Hydroxyindole acetic acid |
False negative with fluorometric test. |
|
Acetone, ketone bodies |
False positive FeCl3 in Gerhardt reaction; red color persists with boiling. |
|
17-OH corticosteroids |
False reduced values with >4.8g q.d. salicylate. |
|
Vanilmandelic acid |
False reduced values. |
|
Uric acid |
May increase or decrease depending on dose. |
|
Prothrombin |
Decreased levels; slightly increased prothrombin time. |
Pregnancy Category C
Salicylic Acid has been shown to be teratogenic in rats and monkeys. It is difficult to extrapolate from oral doses of acetylsalicylic acid used in these studies to topical administration as the oral dose to monkeys may represent six times the maximal daily human dose of salicylic acid when applied topically over a large body surface. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Salicylic Acid Shampoo, 6% should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nursing Mothers
Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from the mother’s use of Salicylic Acid Shampoo, 6% a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother. If used by nursing mothers, it should not be used on the chest area to avoid the accidental contamination of the child.
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Excessive erythema and scaling conceivably could result from use on open skin lesions.
Salicylic Acid Shampoo Dosage and Administration
Wet hair and apply Salicylic Acid Shampoo, 6% to the scalp. Work into a lather then rinse. Repeat the treatment as needed until the condition clears. Once clearing is apparent, the occasional use of Salicylic Acid Shampoo, 6% will usually maintain the remission.
How is Salicylic Acid Shampoo supplied
Salicylic Acid Shampoo, 6% is available as follows:
177 mL plastic bottle (NDC 45802-237-01).
| SALICYLIC ACID
salicylic acid shampoo |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Perrigo New York Inc (078846912) |
| Registrant - L. Perrigo Company (006013346) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Perrigo Israel Pharmaceuticals LTD. | 600093611 | MANUFACTURE(45802-237) | |
Frequently asked questions
More about salicylic acid topical
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Reviews (22)
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- Drug class: topical acne agents
- Breastfeeding
Patient resources
Professional resources
- Salicylic Acid monograph
- Salicylic Acid (FDA)
- Salicylic Acid Foam (FDA)
- Salicylic Acid Gel (FDA)
- Salicylic Acid Liquid (FDA)
Other brands
Salex, Terasic, Virasal, Keralyt Shampoo, ... +6 more